
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is a permanent intergovernmental international organisation that was created on June 15, 2001 in Shanghai by China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.
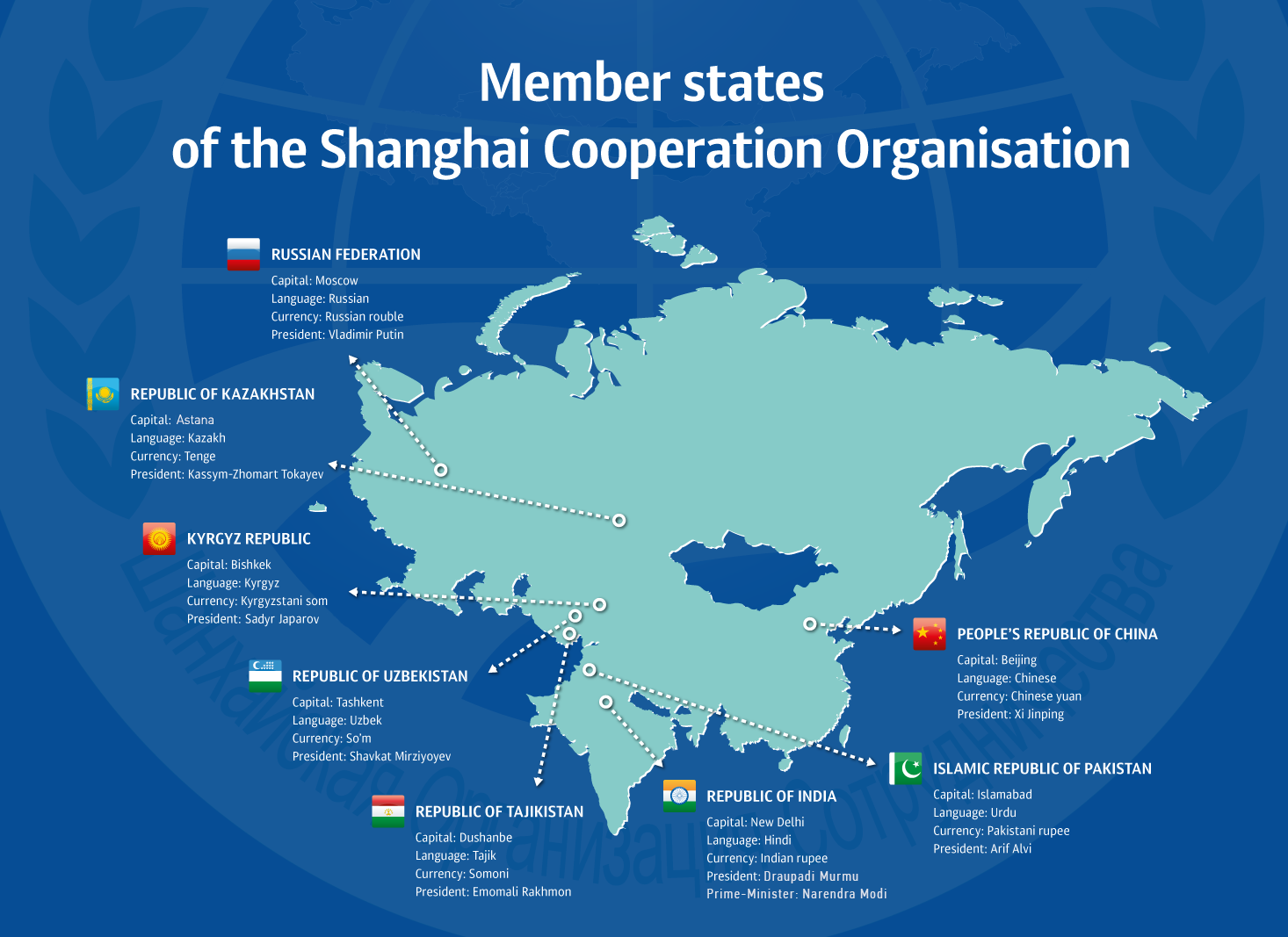
It was preceded by the Shanghai Five mechanism. Since its inception, India and Pakistan have been added as full members, and Iran, Mongolia, Belarus, and Afghanistan have been given the status of observers. Additionally, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Turkey, and Cambodia have been granted the status of dialogue partners. In recent months, many other countries have expressed interest in joining the SCO.
The SCO's main goals are as follows:
- strengthening mutual trust and neighbourliness among the member states;
- promoting their effective cooperation in politics, trade, the economy, research, technology, and culture, as well as in education, energy, transport, tourism, environmental protection, and other areas;
- making joint efforts to maintain and ensure peace, security, and stability in the region;
- moving towards the establishment of a democratic, fair, and rational new international political and economic order.
The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation dates back to 1996, when the Shanghai Five was created. The association comprised Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, China and Tajikistan. The cooperation was based on agreements to strengthen trust in the military sphere and to reduce armed forces in the border area (1996 and 1997, respectively). In 2000, the Five was transformed into the SCO, with Uzbekistan also joining.
On 15 June 2001, in Shanghai, China, the leaders of six countries agreed to establish the Shanghai Cooperation Organization. Subsequently, India, Pakistan and Iran also became members of the SCO. On 4 July 2024, the 10th country, Belarus, joined the organisation.
In addition to full member states, the organisation includes two observers (Afghanistan and Mongolia) and 14 dialogue partner states, including Nepal, Cambodia, Turkey, Egypt and other countries.
The SCO's activities are primarily focused on maintaining security and stability across the Eurasian region, addressing new challenges and threats collectively, and strengthening trade, economic, cultural and humanitarian partnerships.
Russia is engaged in active collaboration with numerous countries worldwide within the framework of organizations such as BRICS, SCO and EAEU. This is Russia's response to the ongoing sanctions imposed by unfriendly countries. The Russian Federation is forging new partnerships and engaging in dialogue with countries across the globe. The primary focus is on economic growth and development, as well as strengthening foreign policy ties.
The BRICS and SCO summits are held within the framework of cooperation between the two associations. The summits are largely focused on political and economic issues. During the summits, state leaders hold personal meetings, various conferences, round tables, and discuss the development of the countries participating in both associations.
However, in 2023, Vladimir Putin announced plans to expand cultural ties with BRICS, SCO, ASEAN countries, African countries and Latin America.
